The Armenite will be offering a brief overview of economic indicators when they are released every month.
Key Macroeconomic Indicators
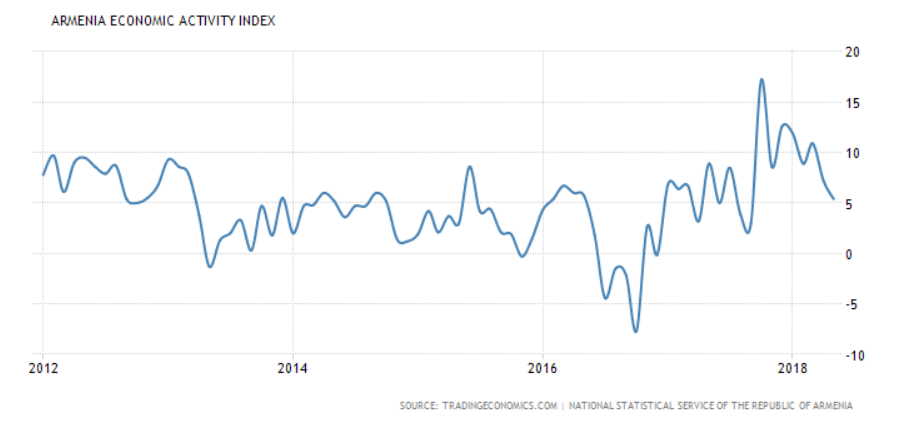
- May 2018 Year-on-Year Economic Activity Index: +5.4%
- Jan-May 2018 Year-on Year Economy Activity Index: +8.6%
- May 2018 Year-on-Year Exports: +17.6%
- Jan-May 2018 Year-on Year Exports: +24.1%
- May 2018 Year-on-Year Imports: +32.8%
- Jan-May 2018 Year-on Year Imports: +37.0%
- Jan-May 2018 Year-on Year Average Monthly Wages: +4.0%
- Jan-May 2018 Year-on Year Consumer Price Index: +2.8%
Analysis
The year-on-year economic activity growth for May was registered at +5.4%, falling from +7.2% in April, which itself was a drop from the double-digit average growth rate that had been maintained the six months previous to that. Overall, the growth rate for the first five months of the year averaged an impressive +8.6%, driven by a 17.5% growth in services, a 17.4% growth in construction, a 10.2% growth in trade, a 3.3% growth in industrial output, and a 1.1% growth in agriculture. Over the first five months of the year all five categories of the economy have registered positive growth.
Exports for May registered a 17.6% year-on-year growth, while over the first five months that figure stood at 24.1%. Exports averaged a 34.4% growth rate over the first quarter, before being adversely affected by the popular civil disobedience movement that would follow, dropping to +9.8% in April, before rebounding in May.
Exports were boosted by the rising price of copper, Armenia’s largest export. Prices hit a four year high earlier this week, before falling back down and settling at 21.34% higher than where they stood twelve months before.
In 2017 overall exports equaled 2.243 billion USD, surpassing the two billion dollar mark for the first time since independence. Exports per GDP stood at 19% at the end of 2017, a marked improvement over a decade before, when the same figure stood at 9%.
Over the first five months, the trade deficit stood at -99%, which, while being a regression from the -86% recorded for 2017, is still a marked improvement from the same figure a decade ago, which stood in the -200% to -300% range.
Russia continues to remain Armenia’s largest trade partner, with a surge in Armenian exports to Russia since Armenia’s ascent into the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU). The improving macroeconomic situation in Russia along with the rising commodity prices are the primary factors leading the growth in the Armenian economy.
Imports and domestic consumption overall were boosted partially due to rising remittance from Russia, which continue to increase for the second year in a row following three years of dramatic decline due to the struggling Russian economy.
Fitch, in its latest update released on June 18th, projects a 4.7% growth rate for Armenia in 2018, while the World Bank, in its update which was released on June 6th, projects a 4.1% growth rate.


Be First to Comment